2025

Multimodal AI generates virtual population for tumor microenvironment modeling
Jeya Maria Jose Valanarasu*, Hanwen Xu*, Naoto Usuyama*, Chanwoo Kim*, Cliff Wong, Peniel Argaw, Racheli Ben Shimol, Angela Crabtree, Kevin Matlock, Alexandra Q. Bartlett, Jaspreet Bagga, Yu Gu, Sheng Zhang, Tristan Naumann, Bernard A. Fox, Bill Wright, Ari Robicsek, Brian Piening, Carlo Bifulco, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
Cell 2025
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) shapes cancer progression and immunotherapy response, but mIF imaging is too expensive and slow for large populations. GigaTIME is a multimodal AI system that generates virtual mIF from routine H&E slides, trained on 40 million cells across 21 proteins. We applied it to 14,256 patients from 51 hospitals, producing 299k virtual mIF slides across 24 cancers and revealing 1,234 significant clinical associations previously impossible to detect. Independent validation on 10,200 TCGA patients confirmed these insights.
Multimodal AI generates virtual population for tumor microenvironment modeling
Jeya Maria Jose Valanarasu*, Hanwen Xu*, Naoto Usuyama*, Chanwoo Kim*, Cliff Wong, Peniel Argaw, Racheli Ben Shimol, Angela Crabtree, Kevin Matlock, Alexandra Q. Bartlett, Jaspreet Bagga, Yu Gu, Sheng Zhang, Tristan Naumann, Bernard A. Fox, Bill Wright, Ari Robicsek, Brian Piening, Carlo Bifulco, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
Cell 2025
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) shapes cancer progression and immunotherapy response, but mIF imaging is too expensive and slow for large populations. GigaTIME is a multimodal AI system that generates virtual mIF from routine H&E slides, trained on 40 million cells across 21 proteins. We applied it to 14,256 patients from 51 hospitals, producing 299k virtual mIF slides across 24 cancers and revealing 1,234 significant clinical associations previously impossible to detect. Independent validation on 10,200 TCGA patients confirmed these insights.

A Cardiac-specific CT Foundation Model for Heart Transplantation
Hanwen Xu, Addie Woicik, Sanaz Asadian, Junbo Shen, Zhengyan Zhang, Ali Nabipoor, J. Peter Musi, Jeffrey Keenan, Maziar Khorsandi, Bassel Al-Alao, Ioannis Dimarakis, Hamid Chalian, Yiing Lin, Daniel Fishbein, Jay Pal, Sheng Wang, Shin Lin
Submitted to Nature Medicine 2025
Heart failure is a leading cause of death, and accurate donor–recipient heart size matching is vital for transplantation success. GigaHeart, trained on 180,897 CT scans, focuses on cardiac regions to achieve state-of-the-art performance across cardiac tasks. It improves heart mass prediction by 33% and reduces sizing errors by 57% compared to traditional equations, enabling more precise donor–recipient matching.
A Cardiac-specific CT Foundation Model for Heart Transplantation
Hanwen Xu, Addie Woicik, Sanaz Asadian, Junbo Shen, Zhengyan Zhang, Ali Nabipoor, J. Peter Musi, Jeffrey Keenan, Maziar Khorsandi, Bassel Al-Alao, Ioannis Dimarakis, Hamid Chalian, Yiing Lin, Daniel Fishbein, Jay Pal, Sheng Wang, Shin Lin
Submitted to Nature Medicine 2025
Heart failure is a leading cause of death, and accurate donor–recipient heart size matching is vital for transplantation success. GigaHeart, trained on 180,897 CT scans, focuses on cardiac regions to achieve state-of-the-art performance across cardiac tasks. It improves heart mass prediction by 33% and reduces sizing errors by 57% compared to traditional equations, enabling more precise donor–recipient matching.
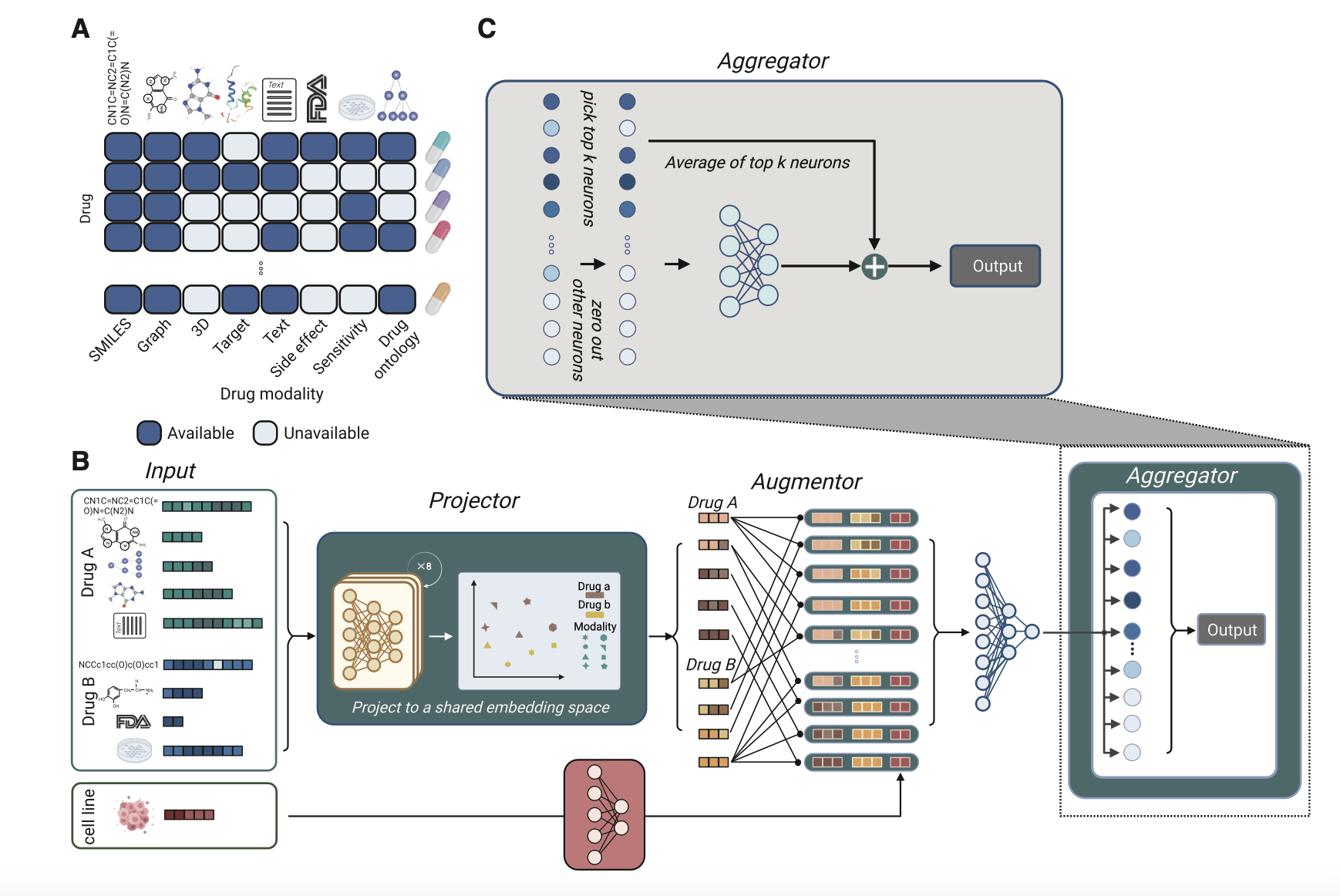
Pisces: A multi-modal data augmentation approach for drug combination synergy prediction
Hanwen Xu*, Jiacheng Lin*, Addie Woicik, Zixuan Liu, Jianzhu Ma, Sheng Zhang, Hoifung Poon, Liewei Wang, Sheng Wang (* equal contribution)
Cell Genomics 2025
The key idea is to augment the sparse dataset by creating multiple views for each drug combination based on different modalities. We combined eight modalities of a drug to create 64 augmented views. By treating each augmented view as a separate instance, Pisces can process any number of drug modalities, circumventing the issue of missing modality.
Pisces: A multi-modal data augmentation approach for drug combination synergy prediction
Hanwen Xu*, Jiacheng Lin*, Addie Woicik, Zixuan Liu, Jianzhu Ma, Sheng Zhang, Hoifung Poon, Liewei Wang, Sheng Wang (* equal contribution)
Cell Genomics 2025
The key idea is to augment the sparse dataset by creating multiple views for each drug combination based on different modalities. We combined eight modalities of a drug to create 64 augmented views. By treating each augmented view as a separate instance, Pisces can process any number of drug modalities, circumventing the issue of missing modality.

A clinically accessible small multimodal radiology model and evaluation metric for chest X-ray findings
Juan Manuel Zambrano Chaves*, Shih-Cheng Huang*, Yanbo Xu*, Hanwen Xu*, Naoto Usuyama, Sheng Zhang, Fei Wang, Yujia Xie, Mahmoud Khademi, Ziyi Yang, Hany Awadalla, Julia Gong, Houdong Hu, Jianwei Yang, Chunyuan Li, Jianfeng Gao, Yu Gu, Cliff Wong, Mu Wei, Tristan Naumann, Muhao Chen, Matthew P Lungren, Akshay Chaudhari, Serena Yeung Levy, Curtis P Langlotz, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
Nature Communications 2025 11,000 downloads
Large foundation models face barriers to clinical adoption due to cost, accessibility, and evaluation limits. LLaVA-Rad, a 7B open-source multimodal model trained on 697K chest X-ray image-text pairs, bridges these gaps—achieving state-of-the-art factual accuracy with a lightweight, scalable, and clinically aligned design.
A clinically accessible small multimodal radiology model and evaluation metric for chest X-ray findings
Juan Manuel Zambrano Chaves*, Shih-Cheng Huang*, Yanbo Xu*, Hanwen Xu*, Naoto Usuyama, Sheng Zhang, Fei Wang, Yujia Xie, Mahmoud Khademi, Ziyi Yang, Hany Awadalla, Julia Gong, Houdong Hu, Jianwei Yang, Chunyuan Li, Jianfeng Gao, Yu Gu, Cliff Wong, Mu Wei, Tristan Naumann, Muhao Chen, Matthew P Lungren, Akshay Chaudhari, Serena Yeung Levy, Curtis P Langlotz, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
Nature Communications 2025 11,000 downloads
Large foundation models face barriers to clinical adoption due to cost, accessibility, and evaluation limits. LLaVA-Rad, a 7B open-source multimodal model trained on 697K chest X-ray image-text pairs, bridges these gaps—achieving state-of-the-art factual accuracy with a lightweight, scalable, and clinically aligned design.
2024

A Multimodal Biomedical Foundation Model Trained from Fifteen Million Image–Text Pairs
Sheng Zhang*, Yanbo Xu*, Naoto Usuyama*, Hanwen Xu*, Jaspreet Bagga, Robert Tinn, Sam Preston, Rajesh Rao, Mu Wei, Naveen Valluri, Cliff Wong, Andrea Tupini, Yu Wang, Matt Mazola, Swadheen Shukla, Lars Liden, Jianfeng Gao, Angela Crabtree, Brian Piening, Carlo Bifulco, Matthew P. Lungren, Tristan Naumann, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
The New England Journal of Medicine, AI 2024 4,500,000 downloads
We present PMC15M, a dataset of 15 million biomedical image text pairs from 4.4 million articles. Trained on PMC15M, BiomedCLIP achieves state of the art performance across diverse biomedical tasks, even surpassing radiology models like BioViL.
A Multimodal Biomedical Foundation Model Trained from Fifteen Million Image–Text Pairs
Sheng Zhang*, Yanbo Xu*, Naoto Usuyama*, Hanwen Xu*, Jaspreet Bagga, Robert Tinn, Sam Preston, Rajesh Rao, Mu Wei, Naveen Valluri, Cliff Wong, Andrea Tupini, Yu Wang, Matt Mazola, Swadheen Shukla, Lars Liden, Jianfeng Gao, Angela Crabtree, Brian Piening, Carlo Bifulco, Matthew P. Lungren, Tristan Naumann, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
The New England Journal of Medicine, AI 2024 4,500,000 downloads
We present PMC15M, a dataset of 15 million biomedical image text pairs from 4.4 million articles. Trained on PMC15M, BiomedCLIP achieves state of the art performance across diverse biomedical tasks, even surpassing radiology models like BioViL.
A whole-slide foundation model for digital pathology from real-world data
Hanwen Xu*, Naoto Usuyama*, Jaspreet Bagga, Sheng Zhang, Rajesh Rao, Tristan Naumann, Cliff Wong, Zelalem Gero, Javier González, Yu Gu, Yanbo Xu, Mu Wei, Wenhui Wang, Shuming Ma, Furu Wei, Jianwei Yang, Chunyuan Li, Jianfeng Gao, Jaylen Rosemon, Tucker Bower, Soohee Lee, Roshanthi Weerasinghe, Bill J. Wright, Ari Robicsek, Brian Piening, Carlo Bifulco, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
Nature 2024 2,000,000 downloads
Prov-GigaPath is a large-scale digital pathology foundation model pretrained on 1.3 billion image tiles from 171,189 whole-slide images across 30,000+ patients and 31 tissue types in the Providence network. Built on a new GigaPath architecture that adapts LongNet for slide-level learning, it enables ultra-large-context modeling of gigapixel pathology slides. Prov-GigaPath achieves state-of-the-art results on 25 of 26 benchmark tasks and demonstrates strong potential for vision–language pathology modeling using real-world data.
A whole-slide foundation model for digital pathology from real-world data
Hanwen Xu*, Naoto Usuyama*, Jaspreet Bagga, Sheng Zhang, Rajesh Rao, Tristan Naumann, Cliff Wong, Zelalem Gero, Javier González, Yu Gu, Yanbo Xu, Mu Wei, Wenhui Wang, Shuming Ma, Furu Wei, Jianwei Yang, Chunyuan Li, Jianfeng Gao, Jaylen Rosemon, Tucker Bower, Soohee Lee, Roshanthi Weerasinghe, Bill J. Wright, Ari Robicsek, Brian Piening, Carlo Bifulco, Sheng Wang, Hoifung Poon (* equal contribution)
Nature 2024 2,000,000 downloads
Prov-GigaPath is a large-scale digital pathology foundation model pretrained on 1.3 billion image tiles from 171,189 whole-slide images across 30,000+ patients and 31 tissue types in the Providence network. Built on a new GigaPath architecture that adapts LongNet for slide-level learning, it enables ultra-large-context modeling of gigapixel pathology slides. Prov-GigaPath achieves state-of-the-art results on 25 of 26 benchmark tasks and demonstrates strong potential for vision–language pathology modeling using real-world data.
2023
Deep flanking sequence engineering for efficient promoter design using DeepSEED
Pengcheng Zhang*, Haochen Wang*, Hanwen Xu*, Lei Wei, Liyang Liu, Zhirui Hu, Xiaowo Wang (* equal contribution)
Nature Communications 2023 Editor highlights
We introduce DeepSEED, an AI-guided framework that integrates expert knowledge with deep learning to design efficient synthetic promoters. DeepSEED improves E. coli and mammalian promoter performance by capturing overlooked flanking-sequence features such as k-mer composition and DNA shape.
Deep flanking sequence engineering for efficient promoter design using DeepSEED
Pengcheng Zhang*, Haochen Wang*, Hanwen Xu*, Lei Wei, Liyang Liu, Zhirui Hu, Xiaowo Wang (* equal contribution)
Nature Communications 2023 Editor highlights
We introduce DeepSEED, an AI-guided framework that integrates expert knowledge with deep learning to design efficient synthetic promoters. DeepSEED improves E. coli and mammalian promoter performance by capturing overlooked flanking-sequence features such as k-mer composition and DNA shape.
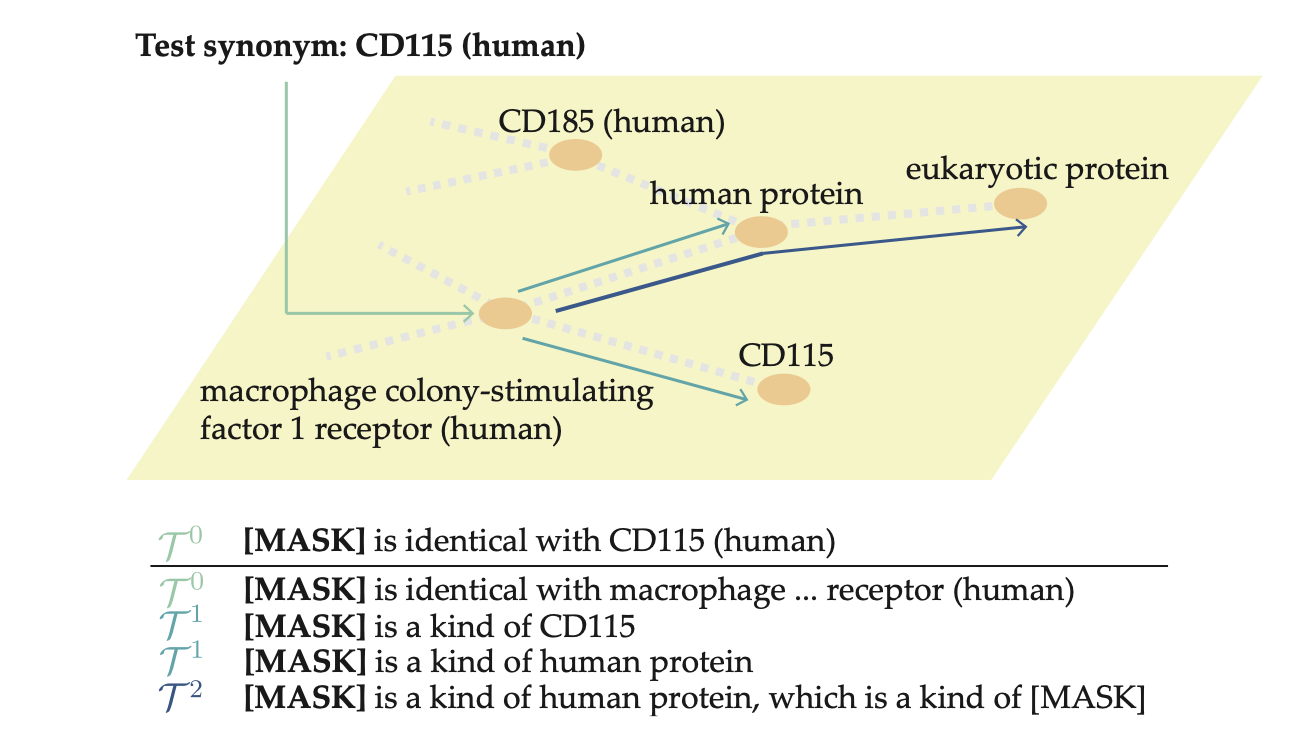
GraphPrompt: Graph-Based Prompt Templates for Biomedical Synonym Prediction
Hanwen Xu*, Jiayou Zhang*, Zhirui Wang*, Shizhuo Zhang, Megh Bhalerao, Yucong Liu, Dawei Zhu, Sheng Wang (* equal contribution)
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2023
Biomedical datasets often contain inconsistent labeling of identical concepts, making manual curation laborious. To address this, we propose the biomedical synonym prediction task and introduce GraphPrompt, a graph-based prompt-learning method that leverages the new OBO-syn dataset of 2 million curated pairs, achieving up to 37.2% improvement over prior approaches.
GraphPrompt: Graph-Based Prompt Templates for Biomedical Synonym Prediction
Hanwen Xu*, Jiayou Zhang*, Zhirui Wang*, Shizhuo Zhang, Megh Bhalerao, Yucong Liu, Dawei Zhu, Sheng Wang (* equal contribution)
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2023
Biomedical datasets often contain inconsistent labeling of identical concepts, making manual curation laborious. To address this, we propose the biomedical synonym prediction task and introduce GraphPrompt, a graph-based prompt-learning method that leverages the new OBO-syn dataset of 2 million curated pairs, achieving up to 37.2% improvement over prior approaches.
Multilingual translation for zero-shot biomedical classification using BioTranslator
Hanwen Xu, Addie Woicik, Hoifung Poon, Russ Altman, Sheng Wang
Nature Communications 2023
BioTranslator introduces a multilingual translation framework that maps free-text biological concepts to non-text data, enabling scientists to interact with biological data without relying on predefined vocabularies. It allows the discovery of novel entities such as cell types and generalizes to tasks like protein function prediction and drug target identification.
Multilingual translation for zero-shot biomedical classification using BioTranslator
Hanwen Xu, Addie Woicik, Hoifung Poon, Russ Altman, Sheng Wang
Nature Communications 2023
BioTranslator introduces a multilingual translation framework that maps free-text biological concepts to non-text data, enabling scientists to interact with biological data without relying on predefined vocabularies. It allows the discovery of novel entities such as cell types and generalizes to tasks like protein function prediction and drug target identification.
2022
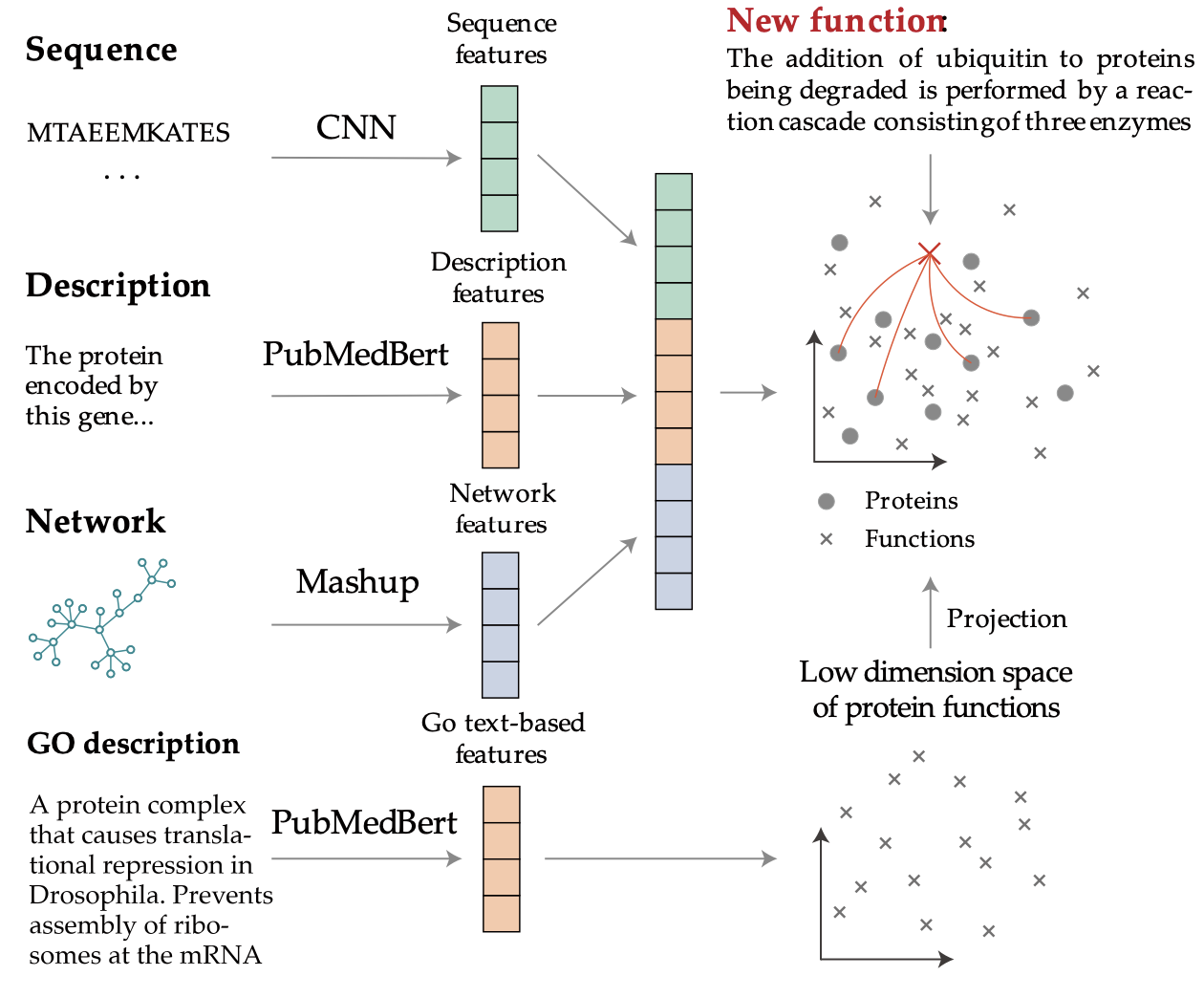
ProTranslator: zero-shot protein function prediction using textual description
Hanwen Xu, Sheng Wang
International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology 2022
Identifying proteins and genes with specific functions is crucial for biomedical research, yet current computational methods struggle to annotate novel functions absent from existing ontologies. We introduce ProTranslator, which reframes protein function prediction as a translation task—from textual function descriptions to protein sequences—enabling zero-shot annotation of unseen functions and paving the way for a protein "search engine" driven by free-text queries.
ProTranslator: zero-shot protein function prediction using textual description
Hanwen Xu, Sheng Wang
International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology 2022
Identifying proteins and genes with specific functions is crucial for biomedical research, yet current computational methods struggle to annotate novel functions absent from existing ontologies. We introduce ProTranslator, which reframes protein function prediction as a translation task—from textual function descriptions to protein sequences—enabling zero-shot annotation of unseen functions and paving the way for a protein "search engine" driven by free-text queries.